
UNIT 1 – ENGLISH VERB SYSTEM.
Time and tense
The notion of time – present, past and future – is universal and independent of any particular language. Time can
be thought of as a line: anything ahead the present moment is in the future, and anything behind it is in the past.
Tense is the grammatical expression of relative time. Thus, the tense of a verb tells us that it is present, past or
future. For example, a present tense does not necessarily express an action taking place in the present time. In
the sentence “Fred will have dinner when his wife arrives home.”, the verb arrives is in the Simple Present Tense;
however, it is used to express a situation that will take place in the future.
Mood
Mood has to do with the emotional attitude of the speaker towards the action. It refers to the factual or non-
factual status of events. Non-factual here means events which do not happen or are only desired. The moods of
English are indicative (or declarative), imperative and subjunctive.
The indicative or declarative mood is a factual mood. It is by far the most frequent mood. It is the usual mood
in declarative and interrogative sentences.
Sally usually watches TV at night. / Did many people attend the meeting yesterday?
The imperative mood is a non-factual mood. The imperative involves the base or plain form (the finite form)
of the verb. We can make an imperative sound politer by using do or please before it. The subject of the verbs
in the imperative is usually “you”, which is generally understood. However, in the “let’s…” construction the
subject is “we”.
It is directive: it covers commands (Get out!), offers (Have a pear.), requests (Please pass me the salt.),
invitations (Come to dinner.), advice (Get your doctor to look at it.), instructions (To see the picture, click here.)
The subjunctive mood is a non-factual mood. It refers to wishes, desires, suggestions. It is used after a very
limited number of verbs -suggest, insist, recommend, demand, wish, imagine, suppose -, and occasionally
after conditional subordinators, expressions of necessity and a limited number of set phrases. There are two
forms of the subjunctive, traditionally called the present and past subjunctive.
PRESENT SUBJUNCTIVE
Mandative subjunctive: used in a that clause after an expression of such notions as demands,
recommendation, proposal, intention contained in subordinate clauses. Even when the verb is in the
past tense, the present subjunctive is used.
They insisted that she consult a psychiatrist, and Laura had the strength to insist that it be a
woman.
We require that all receipts be submitted to the committee for approval.
I suggest that you be careful.
It can also be used in the structure “It is important / essential / vital / advisable... that...”.
It is essential that an adult accompany any child under ten.
NEGATIVE MANDATIVE SUBJUNCTIVE
Regulations require that officers NOT ENTER the scene of the crime.
They ordered that he NOT LEAVE.

PUTATIVE SHOULD (less formal, not subjunctive)
The school ignored my suggestion that Susan SHOULD SIT fewer GCSEs.
They ordered that he SHOULD NOT LEAVE.
Formulaic subjunctive: It consists of the base form and it is only used in clauses in certain set expressions
which have to be learned as wholes. These expressions are usually used in exclamations to express a wish
or hope, very often involving supernatural powers:
Come what may, we will go ahead.
God save the Queen!
So be it.
Suffice it to say…
Damn you!
Peace be with you!
THE WERE SUBJUNCTIVE OR PAST SUBJUNCTIVE
The were-subjunctive is hypothetical or unreal in meaning, being used in adverbial clauses introduced
by such conjunctions as if, if only, as if, as though, and in nominal clauses after verbs like wish, suppose
and imagine. These sentences are called “counterfactual” because they always imply that the
situation described is actually not the case.
If I were you, I´d tell her the truth. / If only I were taller. / He acted as if he were my boss.
ASPECT
The GRAMMATICAL ASPECT may be simple or non-progressive (zero or unmarked), progressive, perfect, and
perfect progressive.
The ASPECTUAL MEANING may be perfective (action complete from the POV of speaker) or imperfective (action
incomplete)
Ann lived in London when I met her.
lived: Simple Past Tense; simple or non-progressive grammatical aspect; imperfective aspectual meaning.
(even though she doesn’t live there now, when I met her the action was incomplete)
met: Simple Past Tense; simple or non-progressive grammatical aspect; perfective aspectual meaning.
(I met her once, the action is complete)
VOICE
It may be active or passive.
LEXICAL & AUXILIARY VERBS
Lexical verbs denote actions, states or events. They are classified into action verbs (drink; cry, walk; remember;
love; et c.), and linking verbs (be; become; feel; stay, remain, etc.)
Auxiliary verbs:
Primary auxiliary verbs: be, have and do. They indicate clause type (e.g. interrogative, negative), aspect
(progressive or perfective), and passive voice. These CAN also be used as lexical verbs.

Secondary or modal auxiliary verbs: core modal verb (can, could, shall, will, would, must, might, may),
semi-modal verbs (dare, need, ought to, used to) and modal expressions (be able to, have (got) to).
These can be used to:
Form questions (subject-auxiliary inversion): Are you leaving?
Form question tags: She looks tired, doesn’t she?
Form negative sentenced by putting not after the operator: She will not / won’t be staying with us.
Form progressive tenses (BE): She is sleeping.
Form perfect tenses (HAVE): She has slept all morning.
Convey emphasis (emphatic positive): A: finish your work / B: I have finished.
Substitute the predicate: A: are you leaving) / B: yes, I am (leaving).
Form the passive voice (BE): The door was opened.
FINITE AND NON-FINITE VERBS.
Finite verbs: they make a group of words into a sentence. It may be an action verb, a linking verb or an auxiliary
verb, and be in its base form, 3
rd
person singular or past simple. Finite verbs can show tense, mood, aspect and
voice. In a finite verb phrase the first or only verb is finite, and the other verbs (if any) are non-finite.
Non-finite verbs: do not show tense or mood, but they are capable of indicating aspect and voice. The non-finite
forms are the infinitive, the “-ing” forms (present participle and gerund) and the past participle. In a non-finite
verb phrase all the verbs are non-finite.
E.G: You could have told me that you were not coming back to help me with the children
COULD
HAVE
TOLD
WERE
COMING
TO HELP
Finite (aux: modal)
Non-finite
(present
participle)
Non-finite
(-ed
participle)
Finite (past
form)
Non-finite
(present
participle)
Non-finite
(TO infinitive)
Auxiliary
(secondary/modal)
Auxiliary
(primary
HAVE)
lexical
Auxiliary
(primary BE)
lexical
lexical

STATIVE AND DYNAMIC VERBS
Stative verbs: their inherent meaning is not easily compatible with the use of the progressive. This is so because
they describe states or situations that we do not expect to change. These verbs describe states (i.e., conditions
that exist, they have no beginning and no end); they do not describe actions. The progressive can occur with
stative verbs, turning the states into events.
COMMON NONPROGRESSIVE VERBS
Some of these verbs describe both a state (stative use) and an action (dynamic use):
VERBS OF EXISTING:
Robert is a fool it’s his nature, it expresses a permanent state STATIVE VERB
Robert is being a fool he is acting foolishly, it’s a temporary situation DYNAMIC VERB
CONTAIN = have or hold smth within itself
IS CONTAINING (her anger) = to control a strong feeling
VERBS OF SENSES:

The verbs HEAR and SEE refer to involuntary reactions which correspond to the deliberate acts of “listening” and
“looking” (voluntary activities). When the verbs FEEL and LOOK are used to refer to physical condition or state,
they can occur freely in the simple present tense or in the progressive form with no change of meaning.
NON CONCLUSIVE VERBS:
These denote various mental perceptions, states of mind or feelings (emotional states). These activities cannot be
started or stopped at will. However, some of these verbs are also commonly used as progressive verbs, with a
difference in meaning:
I believe she is a good teacher “think” STATIVE VERB
She is always believing his lies! Present progressive – Showing annoyance. DYNAMIC VERB
She considers him a good husband. “She finds him …” – STATIVE VERB
I’m considering the idea of travelling to Europe next year. “I’m studying the idea of …” – DYNAMIC VERB
I forgot to tell you something more. STATIVE VERB.
“I failed to remember...” I’m gradually forgetting my English. Developing situation – Increasing or decreasing
activity – DYNAMIC VERB
She imagines herself an old woman. “She believes herself…” STATIVE VERB
She is always imagining she is an old woman. Showing annoyance on part of the speaker. DYNAMIC VERB.
I don’t mind “I don’t care”.- STATIVE VERB
She is minding the baby. “She is taking care of the baby”-DYNAMIC VERB.
I think you are not right. “I believe” - STATIVE VERB
I’m thinking of a new plan. “I’m studying” - DYNAMIC VERB.
What does it mean? “What is the meaning of …?” STATIVE VERB
She is meaning to get a new job. “I’m intending” – DYNAMIC VERB.
I see you are wearing a new suit. “I perceive” – STATIVE VERB
I’m seeing John at the party tonight. “I’m meeting …” DYNAMIC VERB – Future time reference.
Most people love/enjoy eating out “They like in general” – STATIVE VERB. It expresses general preference.
She is loving/enjoying every minute of her holiday. likes specifically (intensify the emotion) – DYNAMIC VERB.
A: How do you like your new job? B: I’m loving it. Occasionally, love and hate can be used in the progressive in
conversation for very strong emphasis.

VERBS SHOWING POSSESION:
They have a cottage in the mountains. “own” – STATIVE VERB
They are having lunch. “eat” – DYNAMIC VERB.
They are having a good time. “experience, undergo” — DYNAMIC VERB.
Some idioms with “have” behaving as action or dynamic verbs:
VERBS OF APPEARANCE:
She appears to be asleep “She seems …” – STATIVE VERB.
She is appearing on the stage. “She is acting …” – DYNAMIC VERB.
OTHER EXISTING VERBS:
This box weighs a lot. “Its weight is …” – STATIVE VERB
The grocer is weighing the fruit “He is finding out the weight of…” – DYNAMIC VERB
That dress fits you perfectly. “It is the right size” – STATIVE VERB.
We are fitting a new carpet in the office. “laying” – DYNAMIC VERB.
The verbs hurt and ache can be used in either the continuous or simple tenses with no difference in meaning.
My head hurts. / My head is hurting. My stomach aches. / My stomach is aching.
USES AND MEANINGS OF THE VERB TENSES
SIMPLE PRESENT
Express permanent actions, timeless actions or eternal truths. The verb is completely timeless; the present is
used without reference to any specific time: there is no limitation on the extension of the state into past and
future. They are statements of what was true in the past, is true now and is likely to be true in future time. It is
found in scientific, mathematical, geographical, proverbial, and other statements made for all time.
Water freezes at 0º C. (scientific statement)
Peru shares a border with Chile. (geographical)
Two and two makes four. (mathematical)
Honesty is the best policy. (proverbial)
Express actions or events which are considered as permanent. In such cases, we can express simple facts, abilities
and continuous states.
60% of robberies occur in big cities. (fact) She plays the piano. (ability) They live in America. (state)

Express habitual actions. The habitual present represents a series of individual events which as a whole make up
a state stretching back into the past and forward into the future. Thus, the verb form indicates an established
habit, a series of repeated events, not just a single one. The action is not necessarily happening at the moment of
speaking. Adverbs of frequency and adverb phrases such as always, generally, every day, are often used to specify
the frequency of the repetition.
Sharon usually gets up at four o’clock. She arrives at the film studio at five and has a coffee.
Express future time reference: it is used to refer to a future action that is considered as very certain to happen. It
is usually called future as a fact, as the possibility of changing this action is out of the question or out of the speaker
control. In many cases, we use it to refer to timetables and programmes. These sentences usually contain future
time words unless the future time reference is given by the context. BOTH THE GRAMMATICAL ASPECT AND THE
ASPECTUAL MEANING ARE IRRELEVANT.
My birthday is tomorrow. Next train leaves at 8:30.
Express an event that happened in the past and is characteristic of narrative style and the popular narrative
conversational style. It describes the past as if were happening now; it conveys something of the dramatic
immediacy of an eye-witness account. It occurs largely in conversation in which it gives a sense of immediacy to a
past event. It can also be found in newspaper headlines reporting recent events, as the essence of news coverage
is its immediacy. Framing the bold headline statements in the present tense gives them a sense of urgency and
excitement that is thought to be more enticing to the reader.
At that moment in comes a messenger from the Head office, telling me the boss wants to see me in a hurry.
“BABY STARTS FIRE”
PRESENT PROGRESSIVE
Indicate an activity in progress at the moment of speaking or around the time of speaking. The action began in
the recent past, is continuing at present and will probably end at some point of time in the future. The three main
characteristics of the progressive aspect: incompleteness, temporariness and emphasis on duration are present.
Time adverbs such as right now, currently emphasize the immediacy of the ongoing action.
A: What are you doing? B: I’m watching TV right now.
Refer to an action that is habitual or repeated, but for or over a limited period of time. They are temporary
actions that are going on around now, but not at the actual moment of speaking. Adverbs of time, such as these
days, are essential to denote this meaning.
They are eating out this week because they are having their kitchen redecorated.
Refer to an action that is repeated more often than expected. There’s usually (though not necessarily)
annoyance, irritation, disapproval on the part of the speaker. In this case, it loses its semantic component of
temporariness. Adverbs of frequency such as for ever, constantly are used to reinforce the idea of repetition and
to describe and emphasize a never ending series of events.
He is always calling me to ask some silly question.
Express changing situations or states developing into other states. The verb indicates “increase” or “decrease”
in the activity. It is usually used with such comparative adverbials, adjectives or quantifiers as more and more,
little by little, worse and worse, etc.
More and more forests are disappearing because of fire.

Indicate an activity which has been arranged, beforehand, for the near future. It has to be contextualized by
adverbs and other time expressions.
I’m coming back in a few minutes. I’m seeing the doctor next Tuesday.
PRESENT PERFECT
Refer to an activity or state which begins in the past and continues up to the moment of speaking. The activity
has not finished yet, so the time of the action is past and present. The adverbial phrases/clauses are obligatory
because their omission changes the meaning. This is called the “Unfinished use of the Present Perfect”.
Jane has lived in Scotland since 1980 / for 40 years / so far.
A habit or repeated event -usually shown by adverbs of frequency- in a period of time leading up to
the present is also expressed by this use of the Present Perfect. The action or event may go on into
the future.
She has often worked at night until now.
Express an action that began and finished in the past. The time is not specified at all. We talk about the past
without any reference to time because the time is not important or not known or imprecise. Using the Present
Perfect rather than the Simple Past shows that the past is irrelevant to a present situation: we are interested in
the results of the action. The connection with the past action is valid and important for the speaker. This is usually
called “the finished use of the Present Perfect”.
I’ve finished my work; now I can sit and rest.
Indicate an activity completed in the immediate, recent - but also indefinite - past time. The action took place a
short time ago. The adverbials just, lately and recently emphasize recency.
I have just had lunch.
Refer to an action that happened (or never happened) before now, at an indefinite, unspecified time in the
past. The exact time when the action happened is not important.
Have you ever been to America? I have already had lunch. I haven’t had lunch yet.
Denote an action that was completed during a present incomplete period of time; the period of time is not over
at the moment of speaking. We generally use adverbs or adverbial phrases such as today, this week, this year, etc.
as these expressions denote a period of time that refers partly to the past and partly to the present.
We’ve done very little today.
Describe or talk about a specific number of times we have completed or done something in the past; the exact
time when the action took place is not mentioned.
I’ve smoked ten cigarettes.
Convey future time reference in adverbial clauses of time or condition.
You will be able to play with your friends once / if you have done your homework.
Please, don’t leave until everybody has finished eating.

PRESENT PERFECT PROGRESSIVE
Indicate an activity which started in the past and is still in progress at the time of speaking. The action may or
may not go on into the future. It puts emphasis on the duration of the action and on the imperfective meaning
You have been sleeping for ten hours.
Indicate a (temporary) habit which started in the past and has continued up to the present.
Lucy has been walking to work this week.
If the verb is not accompanied by an adverbial of duration, the implication is often that the effects of the
happening are still visible, that is to say, the action has effects which are still apparent. The action started in the
past and lasted for some time. The action may have finished or may still be going on.
You’ve been fighting again; you’ve got a black eye.
SIMPLE PAST
It takes place before the present moment and the speaker has a definite time in mind.
Denotes activities or states in the past without any connection with the present. We are interested in when the
action took place so we usually use adverbial expressions that indicate the specific point in time when the action
was carried out.
Last night we ate dinner in that Italian restaurant you like so much.
Indicate a definite period of past time.
He drove along the motorway for two hours.
Express past habits or states that are now finished.
Paul practised every day until he could hit his own mark.
PAST PROGRESSIVE
We use it when we are interested mainly in the past activity and in the duration of it. It is used to express a single
activity in progress in the past. We do not mention when the action started or finished. The three main
characteristics are present: incompleteness, temporariness and duration (action in progress).
It was raining hard.
Indicate that an action was repeated (but not permanent) over a limited period of time.
She was eating only one meal a day those days.
Indicate repeated and sporadic past actions that show (though not necessarily) annoyance, irritation,
disapproval, exasperation on the part of the speaker. Adverbs of frequency are usually used to reinforce the idea
of repetition.
She was always borrowing my books.

PAST PERFECT
Refers to a past action previous to another past action or stated time in the past. It is used to express “past in
the past”. It is also called “EARLIER PAST”.
She had begun her studies when I met her.
Denote an incomplete past action that had started before another past action and had lasted for some time.
He had been unconscious for several hours when we found him.
Express an action which had started and finished in the past and whose results were visible in the past. This is
the “RESULTATIVE PAST IN THE PAST”.
Bill had injured his legs in a car accident, so he had to use a wheelchair for six months.
PAST PERFECT PROGRESSIVE
It is used to put emphasis on the duration of an action which started in the past and finished in the past before
another past action or a stated time in the past, usually with “for” or “since” or with an adverbial clause of time.
He had been waiting long before she arrived.
RESULTATIVE PAST IN THE PAST: express an action which lasted for some time in the past and whose duration
caused visible results later on in the past.
She had been shouting all day, so that night she couldn’t speak.
SIMPLE FUTURE
We can use the auxiliary “will” to talk about an action or activity that has been planned for the future. In formal
style, “will” is used to talk about future events that have been previously arranged in some detail.
Where will you stay in Berlin? The meeting will begin at noon.
We use “will” to tell about an action, a state or event that is definitely going to happen in the future.
Aunt Catherine will be 90 next week.
Express “on-the-spot decisions”, that is to say, decisions we make at the time of speaking. It actually represents
the process of decision-making.
There is Sonia. I´ll go and talk to her.
Express promises, threats, warnings, hopes, fears, invitations, refusal, willingness.
I promise I will be punctual next time. He will not stop smoking although you insist.
Requests and offers.
A: I don’t understand this exercise. Will you help me? B: Yes, of course; I will explain it to you in a minute.

FUTURE PROGRESSIVE
Indicate an action that will be taking place, in progress (imperfective aspectual meaning), at a certain, stated
time in the future. Sometimes, it is used to refer to situations which are part of the normal course of events or
that are one of a repeated or regular series of events.
I will be travelling to London when you wake up tomorrow.
In certain contexts, there is no difference in meaning between this particular use of the Future Progressive tense
and the use of the Present Progressive tense when used to refer to future actions that are arranged beforehand.
I´m flying / will be flying to Madrid tomorrow morning as arranged.
FUTURE PERFECT
Refer to an action that will have been completed prior to or by (not later than) a certain time in the future.
When we use this structure, we think of a future time and look back from that future time to say that something
will be complete.
I will have finished grading the papers before 4.00 p.m.
FUTURE PERFECT PROGRESSIVE
Refer to an action that began before a certain future time, but will not have been completed by then. It is used
to emphasize the duration of an action up to a certain time in the future. The action may continue further.
By the end of the year, they will have been working on that project for ten months.
BE GOING TO
Future fulfilment of a present intention / plan / ambition: the speaker has the firm intention of performing or
fulfilling an action.
I’m going to look for a new place to live next month.
Future fulfilment of a present cause or evidence: show the future culmination of a present cause. It is used in
predictions where there is evidence in the present time that something will happen in the near future.
There is going to be a storm in a minute. (I can see black clouds gathering).
UNIT 2 – CLAUSE ELEMENTS.
THE SUBJECT
The head of a Noun Phrase [NP] may be a noun or a noun equivalent or a nominal.
[COMMON NOUN] Birds fly
[NOMINAL ADJECTIVES] The retired suffer a lot.
[PROPER NOUN] Shakespeare wrote Hamlet.

TEMPORAL July is a very cold month in our country.
INDEPENDENT GENITIVE Martin’s was a clear example.
[PERSONAL PRONOUN] They have been playing cards since two o’clock
[INDEFINITE PRONOUN] Somebody has sent her a dozen roses
[DEMONSTRATIVE PRONOUN] This is my last word.
[POSSESSIVE PRONOUN] Mike’s is an old car, but mine is even older.
[INTERROGATIVE PRONOUN] Who is talking at the back?
[PRONOMINAL GROUP] One of the students left the classroom
[INFINITIVE PHRASE] To see is to believe.
[GERUNDIAL PHRASE] Swimming is good exercise.
NOUN PHRASE [(PREMODIFIERS) + HEAD + (POSTMODIFIERS)] Little girls like playing with dolls.
UNDERSTOOD Listen to me, please. (You)
GRAMMATICAL SUBJECTS
THE EXISTENTIAL THERE AND THE NOTIONAL SUBJECT
EXISTENTIAL or NONREFERENTIAL THERE: THERE fills the subject position and does not refer to anything
previously mentioned.
There is a unicorn in the garden. (= A unicorn is in the garden.)
There were some noisy children outside. (= Some noisy children were outside.)
THE INTRODUCTORY OR ANTICIPATORY IT
It is used when we want or need to anticipate the subject, generally when the subject is long. The Anticipatory IT
has no meaning and merely performs a grammatical function. The resulting syntactic construction has two
subjects: the “anticipatory” or “introductory” subject and the “Postponed” or “Real” subject, which is the actual
carrier of meaning.
It’s lovely not to worry about the weather.
It’s great eating in a different restaurant every night.
IT AS DUMMY / NON-REFERENTIAL OR SEMANTICALLY EMPTY SUBJECT.
In such cases, “it” carries no information, so we call it an “empty subject” or “dummy it”. It can also be called
“non-referential subject” because it appears to have no clearly definable antecedent. We can use “it” to refer to:
Weather / atmospheric conditions: It’s too windy in Chicago.
Environment: It’s too cold in my room.
Time: It’s getting late.
Distance: It seems far from here to the mountains. How far is it to Oxford?

THE VERB PHRASE
It expresses the action or state to which other elements relate, and it controls the other kinds of elements and
meanings that can be in the clause.
THE OBJECT
An object is a noun phrase; it usually follows the verb and it only occurs with transitive verbs. It occurs with the
monotransitive pattern and the ditransitive pattern.
THE PREDICATIVE
A predicative can be an adjectival phrase or a noun phrase. It follows the verb phrase and (if one is present) the
direct object. There are two major types of predicative: the subject complement and the object complement.
ADVERBIALS
OBLIGATORY ADVERBIALS: Some verbs take an adverbial to complete their meaning. This is known as an
obligatory adverbial. Obligatory adverbials can occur with two patterns: the copular pattern and the
complex transitive pattern. Obligatory adverbials usually express place or direction although they can also
express time or manner meanings, as in:
Classes start in April.
She placed the baby on a blanket in the living room.
She treated him very badly.
OPTIONAL ADVERBIALS: they can be added to clauses with any type of verb. They are usually adverbial
phrases, prepositional phrases or noun phrases. More than one optional adverbial can occur in a simple
clause. They are rather loosely attached to the rest of the clause: whereas the verb phrase is central, the
optional adverbial is relatively peripheral. The adverbial could be omitted without making the clause
structurally incomplete, but it still causes a difference in meaning. Optional adverbials add extra, further
information to the clause, such as place, time, manner, extent, and attitude:
Personally, I don’t like it. (attitude)
She loves him very deeply. (manner)
Stella has been working hard in her office since eight in the morning. (manner, place, time)
BASIC SENTENCE PATTERNS
A verb is intransitive (Vi) when the action denoted by the verb does not pass over from the subject to anything
else (only the subject suffers the action). When information about manner, place or time is not essential, it’s not
considered to be part of the pattern, so it’s an optional adverbial.

If the main verb requires a direct object to complete the sentence, it is a transitive verb. The direct object refers
to a person or thing directly affected by the action described in the sentence. A verb is called monotransitive
(VMT) when it takes only one object (the direct object).
Often, the people we are talking to know what the object is because of the situation, or because the object has
already been mentioned. In this case, we can omit the object, even though the verb is transitive.
(a car)
(cigarettes)
(the question)
THE COGNATE OBJECT
It allows to make a verb which is usually intransitive (lacking any object), transitive. It is an object alike to the verb;
it is formed from the same root as the verb.
!!
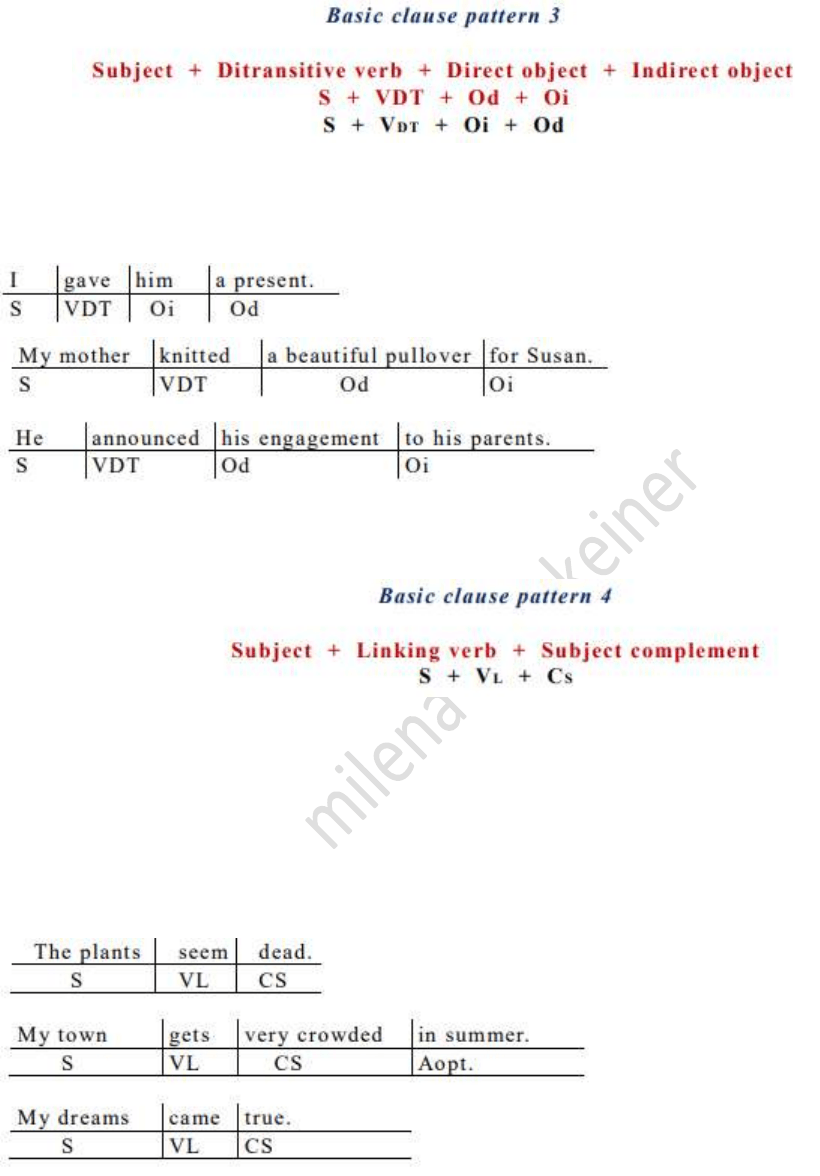
A verb is ditransitive (VDT) when it takes both a direct and an indirect object (who or what benefits from an action).
In some cases, the indirect object uses the connecting preposition “to” or “for”; in some cases, there is no
connecting preposition.
If a verb requires a subject complement (Cs) to complete the sentence, the verb is a linking verb. The subject
complement typically identifies or characterizes the person or thing denoted by the subject. The subject
complement is typically a noun phrase or an adjectival phrase. The subject complement is an obligatory
constituent in the sense that it completes the meaning of the verb.
A copula or linking verb is a verb that links the subject and the complement of a clause: “be”, “seem”, “become”,
“look”, “stay”, “keep”, “remain”, “get”, “make”, “taste”, “sound”.
Este documento contiene más páginas...
Descargar Completo
RESUMEN GRAMATICA UNITS 12345.pdf
 Estamos procesando este archivo...
Estamos procesando este archivo...
 Lamentablemente la previsualización de este archivo no está disponible. De todas maneras puedes descargarlo y ver si te es útil.
Lamentablemente la previsualización de este archivo no está disponible. De todas maneras puedes descargarlo y ver si te es útil.
Descargar
 Estamos procesando este archivo...
Estamos procesando este archivo...
 Lamentablemente la previsualización de este archivo no está disponible. De todas maneras puedes descargarlo y ver si te es útil.
Lamentablemente la previsualización de este archivo no está disponible. De todas maneras puedes descargarlo y ver si te es útil.